All Topics
Linked List
Before understanding the linked list concept, we first look at why there is a need for a linked list.
There are two major drawbacks of using array:
We cannot insert more than the specified number of elements because only that much spaces are allocated for the elements.
In the case of an array, lots of wastage of memory can occur.
For example, if we declare an array of 50 size but we insert only 10 elements in an array.
So, in this case, the memory space for other 40 elements will get wasted and cannot be used by another variable as this whole space is occupied by an array.
In array, we are providing the fixed-size at the compile-time, due to which wastage of memory occurs.
The solution to this problem is to use the linked list.
Linked List:-
A linked list can be defined as the collection of the nodes in which one node is connected to another node,
and node consists of two parts, i.e., one is the data part and the second one is the address part.
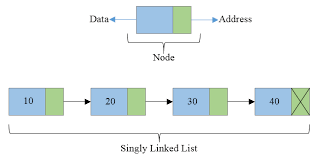 In the above figure, we can observe that each node contains the data and the address of the next node.
In the above figure, we can observe that each node contains the data and the address of the next node.
The last node of the linked list contains the NULL value in the address part.
How can we declare the Linked list??
the linked list contains two parts, which are of two different types, i.e.,
one is a simple variable, and the second one is a pointer variable.
We can declare the linked list by using the user-defined data type known as structure.
Advantages of using a Linked list over Array
Dynamic data structure:
The size of the linked list is not fixed as it can vary according to our requirements.
Insertion and Deletion:
Insertion and deletion in linked list are easier than array as the elements in an array are stored in a consecutive location.
In contrast, in the case of a linked list, the elements are stored in a random location.
The complexity for insertion and deletion of elements from the beginning is O(1) in the linked list, while in the case of an array, the complexity would be O(n).
If we want to insert or delete the element in an array, then we need to shift the elements for creating the space.
On the other hand, in the linked list, we do not have to shift the elements.
In the linked list, we just need to update the address of the pointer in the node.
Memory efficient:-
Its memory consumption is efficient as the size of the linked list can grow or shrink according to our requirements.
Implementation:-
Both the stacks and queues can be implemented using a linked list.
Disadvantages of Linked list
Memory usage:-
The node in a linked list occupies more memory than array as each node occupies two types of variables, i.e.,
one is a simple variable, and another is a pointer variable that occupies 4 bytes in the memory.
Traversal:-
In a linked list, the traversal is not easy. If we want to access the element in a linked list,
we cannot access the element randomly, but in the case of an array,
we can randomly access the element by index. For example, if we want to access the 3rd node,
then we need to traverse all the nodes before it. So, the time required to access a particular node is large.
Reverse traversing
In a linked list, backtracking or reverse traversing is difficult.
In a doubly linked list, it is easier but requires more memory to store the back pointer.
Operations that can be performed on Linked List:-
Traversing;
Searching;
Insertion - at the end, in the middle, at the front;
Deletion - from the end, from the middle, from the front;